
蓝桥杯 2017 年 javaB 组真题刷题笔记
2023/3/9大约 12 分钟
蓝桥杯 2017 年 javaB 组真题刷题笔记
目录
_01_购物单
第八届蓝桥杯【省赛试题第一题】
标题: 购物单
小明刚刚找到工作,老板人很好,只是老板夫人很爱购物。老板忙的时候经常让小明帮忙到商场代为购物。小明很厌烦,但又不好推辞。
这不,XX大促销又来了!老板夫人开出了长长的购物单,都是有打折优惠的。
小明也有个怪癖,不到万不得已,从不刷卡,直接现金搞定。
现在小明很心烦,请你帮他计算一下,需要从取款机上取多少现金,才能搞定这次购物。
取款机只能提供100元面额的纸币。小明想尽可能少取些现金,够用就行了。
你的任务是计算出,小明最少需要取多少现金。
以下是让人头疼的购物单,为了保护隐私,物品名称被隐藏了。
-----------------
**** 180.90 88折
**** 10.25 65折
**** 56.14 9折
**** 104.65 9折
**** 100.30 88折
**** 297.15 半价
**** 26.75 65折
**** 130.62 半价
**** 240.28 58折
**** 270.62 8折
**** 115.87 88折
**** 247.34 95折
**** 73.21 9折
**** 101.00 半价
**** 79.54 半价
**** 278.44 7折
**** 199.26 半价
**** 12.97 9折
**** 166.30 78折
**** 125.50 58折
**** 84.98 9折
**** 113.35 68折
**** 166.57 半价
**** 42.56 9折
**** 81.90 95折
**** 131.78 8折
**** 255.89 78折
**** 109.17 9折
**** 146.69 68折
**** 139.33 65折
**** 141.16 78折
**** 154.74 8折
**** 59.42 8折
**** 85.44 68折
**** 293.70 88折
**** 261.79 65折
**** 11.30 88折
**** 268.27 58折
**** 128.29 88折
**** 251.03 8折
**** 208.39 75折
**** 128.88 75折
**** 62.06 9折
**** 225.87 75折
**** 12.89 75折
**** 34.28 75折
**** 62.16 58折
**** 129.12 半价
**** 218.37 半价
**** 289.69 8折
需要说明的是,88折指的是按标价的88%计算,而8折是按80%计算,余者类推。
特别地,半价是按50%计算。
请提交小明要从取款机上提取的金额,单位是元。
答案是一个整数,类似4300的样子,结尾必然是00,不要填写任何多余的内容。
特别提醒:不许携带计算器入场,也不能打开手机。编程实现:利用正则表达式实现
import java.lang.reflect.Array;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.Arrays;
import java.util.Scanner;
public class _01_购物单 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
double total = 0;
while (true) {
String str = sc.nextLine();
if (str.equals("break"))
break;
String[] strs = str.replaceAll("[ ]+", ",").split(",");
double price = Double.valueOf(strs[1]);
double discount = 1;
if (strs[2].startsWith("半")) {
discount = 0.5;
} else if (strs[2].length() == 2) {
discount = Double.valueOf(strs[2].substring(0, 1)) / 10d;
} else if (strs[2].length() == 3) {
discount = Double.valueOf(strs[2].substring(0, 2)) / 100d;
} else {
System.out.println("error!!!!!!!!!");
break;
}
System.out.println(price);
System.out.println(discount);
total += price * discount;
}
System.out.println(total);
// 输出:5136.859500000001
}
}_02_纸牌三角形

public class _02_纸牌三角形 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
dfs(0);
System.out.println(counter / (3 * 2));// 可旋转3次,镜像两次。
}
static int data[] = { 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9 };
static int counter = 0;
static void dfs(int curStep) {
if (curStep == data.length) {
if (check()) {
counter++;
}
} else {
for (int i = curStep; i < data.length; i++) {
swap(data, curStep, i);
dfs(curStep + 1);
swap(data, curStep, i);
}
}
}
static boolean check() {
int i = data[0] + data[1] + data[2] + data[3];
int j = data[3] + data[4] + data[5] + data[6];
int k = data[6] + data[7] + data[8] + data[0];
return i == j && j == k;
}
static void swap(int[] arr, int i, int j) {
if (i != j) {
arr[i] = arr[i] ^ arr[j];
arr[j] = arr[i] ^ arr[j];
arr[i] = arr[i] ^ arr[j];
}
}
}_03_承压计算
题目描述 :
X星球的高科技实验室中整齐地堆放着某批珍贵金属原料。
每块金属原料的外形、尺寸完全一致,但重量不同。
金属材料被严格地堆放成金字塔形。
7
5 8
7 8 8
9 2 7 2
8 1 4 9 1
8 1 8 8 4 1
7 9 6 1 4 5 4
5 6 5 5 6 9 5 6
5 5 4 7 9 3 5 5 1
7 5 7 9 7 4 7 3 3 1
4 6 4 5 5 8 8 3 2 4 3
1 1 3 3 1 6 6 5 5 4 4 2
9 9 9 2 1 9 1 9 2 9 5 7 9
4 3 3 7 7 9 3 6 1 3 8 8 3 7
3 6 8 1 5 3 9 5 8 3 8 1 8 3 3
8 3 2 3 3 5 5 8 5 4 2 8 6 7 6 9
8 1 8 1 8 4 6 2 2 1 7 9 4 2 3 3 4
2 8 4 2 2 9 9 2 8 3 4 9 6 3 9 4 6 9
7 9 7 4 9 7 6 6 2 8 9 4 1 8 1 7 2 1 6
9 2 8 6 4 2 7 9 5 4 1 2 5 1 7 3 9 8 3 3
5 2 1 6 7 9 3 2 8 9 5 5 6 6 6 2 1 8 7 9 9
6 7 1 8 8 7 5 3 6 5 4 7 3 4 6 7 8 1 3 2 7 4
2 2 6 3 5 3 4 9 2 4 5 7 6 6 3 2 7 2 4 8 5 5 4
7 4 4 5 8 3 3 8 1 8 6 3 2 1 6 2 6 4 6 3 8 2 9 6
1 2 4 1 3 3 5 3 4 9 6 3 8 6 5 9 1 5 3 2 6 8 8 5 3
2 2 7 9 3 3 2 8 6 9 8 4 4 9 5 8 2 6 3 4 8 4 9 3 8 8
7 7 7 9 7 5 2 7 9 2 5 1 9 2 6 5 3 9 3 5 7 3 5 4 2 8 9
7 7 6 6 8 7 5 5 8 2 4 7 7 4 7 2 6 9 2 1 8 2 9 8 5 7 3 6
5 9 4 5 5 7 5 5 6 3 5 3 9 5 8 9 5 4 1 2 6 1 4 3 5 3 2 4 1
x x x x x x x x x x x x x x x x x x x x x x x x x x x x x x
其中的数字代表金属块的重量(计量单位较大)。 最下一层的X代表30台极高精度的电子秤。
假设每块原料的重量都十分精确地平均落在下方的两个金属块上, 最后,所有的金属块的重量都严格精确地平分落在最底层的电子秤上。
电子秤的计量单位很小,所以显示的数字很大。
工作人员发现,其中读数最小的电子秤的示数为: 2086458231
请你推算出:读数最大的电子秤的示数为多少?
注意:需要提交的是一个整数,不要填写任何多余的内容。
题目大意:
已知某个读数最小的电子秤为:2086458231,问读数最大的电子秤是多少。思路
7 // 7的重量均匀落在5和8上
5 8
7 8 8
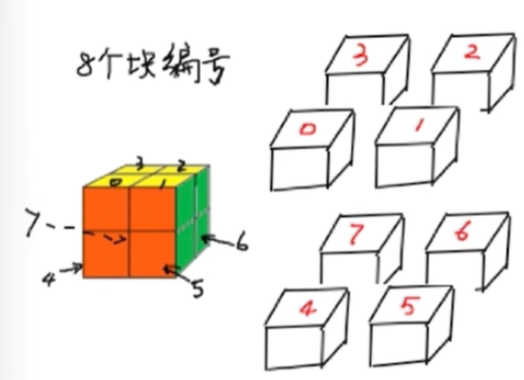
9 2 7 2_04_魔方状态
_05_取数位
题目描述
求1个整数的第k位数字有很多种方法。
以下的方法就是一种。
public class Main
{
static int len(int x){
if(x<10) return 1;
return len(x/10)+1;
}
// 取x的第k位数字
static int f(int x, int k){
if(len(x)-k==0) return x%10;
return ______填空______; // 递归即可,答案: f(x/10,k)
}
public static void main(String[] args)
{
int x = 23513;
System.out.println(f(x,3));
}
}_06_最大公共子串
最大公共子串长度问题就是:
求两个串的所有子串中能够匹配上的最大长度是多少。
比如:“abcdkkk” 和 “baabcdadabc”,
可以找到的最长的公共子串是"abcd",所以最大公共子串长度为4。
下面的程序是采用矩阵法进行求解的,这对串的规模不大的情况还是比较有效的解法。
public class Main
{
static int f(String s1, String s2)
{
char[] c1 = s1.toCharArray();
char[] c2 = s2.toCharArray();
int[][] a = new int[c1.length+1][c2.length+1];
int max = 0;
for(int i=1; i<a.length; i++){
for(int j=1; j<a[i].length; j++){
if(c1[i-1]==c2[j-1]) {
a[i][j] = __________________; //填空 : a[i-1][j-1]+1
if(a[i][j] > max) max = a[i][j];
}
}
}
return max;
}
public static void main(String[] args){
int n = f("abcdkkk", "baabcdadabc");
System.out.println(n);
}
}_07_日期问题
题目描述
小明正在整理一批历史文献。这些历史文献中出现了很多日期。小明知道这些日期都在 1960 年 1 月 1 日至 2059 年 12 月 31 日。令小明头疼的是,这些日期采用的格式非常不统一,有采用年/月/日的,有采用月/日/年的,还有采用日/月/年的。
更加麻烦的是,年份也都省略了前两位,使得文献上的一个日期,存在很多可能的日期与其对应。
比如 02/03/04,可能是 2002 年 03 月 04 日、2004 年 02 月 03 日或 2004 年 03 月 02 日。
给出一个文献上的日期,你能帮助小明判断有哪些可能的日期对其对应吗?
输入描述
一个日期,格式是 "AA/BB/CC" ( 0≤A,B,C≤9)。
输出描述
输出若干个不相同的日期,每个日期一行,格式是 "yyyy-MM-dd"。多个日期按从早到晚排列。
输入输出样例
示例输入
02/03/04
输出
2002-03-04
2004-02-03
2004-03-02import java.util.HashSet;
import java.util.Scanner;
import java.util.Set;
/**
* _07_日期问题
*/
public class _07_日期问题 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
String info = sc.nextLine();
int aa = Integer.parseInt(info.substring(0, 2));
int bb = Integer.parseInt(info.substring(3, 5));
int cc = Integer.parseInt(info.substring(6, 8));
// System.out.println(aa);
// System.out.println(bb);
// System.out.println(cc);
check(1900 + aa, bb, cc);
check(2000 + aa, bb, cc);
check(1900 + cc, aa, bb);
check(2000 + cc, aa, bb);
check(1900 + cc, bb, aa);
check(2000 + cc, bb, aa);
// 集合自带排序和去重
for (String item : res) {
System.out.println(item);
}
}
static Set<String> res = new HashSet<>();
static void check(int yyyy, int mm, int dd) {
if (1960 <= yyyy && yyyy <= 2059 &&
1 <= mm && mm <= 12 &&
1 <= dd && dd <= 31) {
switch (mm) {
case 2:
if (isLeaf(yyyy) && dd <= 29) {
break;
} else if (dd <= 28) {
break;
} else {
return;
}
// 4 6 9 11月:30天,
// 2月:润29 平28
// 其他月:31天
case 4:
case 6:
case 9:
case 11:
if (dd <= 30)
break;
else
return;
}
String k = yyyy + "-" + (mm <= 9 ? "0" + mm : mm) + "-" + (dd <= 9 ? "0" + dd : dd);
res.add(k);
}
}
static boolean isLeaf(int yyyy) {
return yyyy % 400 == 0 || (yyyy % 4 == 0 && yyyy % 100 != 0);
}
}_08_包子凑数
题目:
小明几乎每天早晨都会在一家包子铺吃早餐。他发现这家包子铺有 N 种蒸笼,其中第 i 种蒸笼恰好能放Ai 个包子。每种蒸笼都有非常多笼,可以认为是无限笼。
每当有顾客想买 X 个包子,卖包子的大叔就会迅速选出若干笼包子来,使得这若干笼中恰好一共有 X 个包子。比如一共有 3 种蒸笼,分别能放 3、4 和 5 个包子。当顾客想买 11 个包子时,大叔就会选 2 笼 3 个的再加 1 笼 5 个的(也可能选出 1 笼 3 个的再加 2 笼 4 个的)。
当然有时包子大叔无论如何也凑不出顾客想买的数量。比如一共有 3 种蒸笼,分别能放 4、5 和 6 个包子。而顾客想买 7 个包子时,大叔就凑不出来了。
小明想知道一共有多少种数目是包子大叔凑不出来的。
输入描述
第一行包含一个整数 N (1≤N≤100)。
以下 N 行每行包含一个整数 Ai (1≤Ai≤100)。
输出描述
一个整数代表答案。如果凑不出的数目有无限多个,输出 INF。
输入输出样例
示例 1
输入
2
4
5
输出
6
样例说明
凑不出的数目包括:1, 2, 3, 6, 7, 11。
示例 2
输入
2
4
6
输出
INF
样例说明
所有奇数都凑不出来,所以有无限多个
运行限制
最大运行时间:1s
最大运行内存: 256M_09_分巧克力
_10_K倍区间
K倍区间
题目描述:
给定一个长度为 N 的数列,A1,A2,…AN,如果其中一段连续的子序列 Ai,Ai+1,…Aj 之和是 K 的倍数,我们就称这个区间 [i,j] 是 K 倍区间。
你能求出数列中总共有多少个 K 倍区间吗?
输入格式
第一行包含两个整数 N 和 K。
以下 N 行每行包含一个整数 Ai。
输出格式
输出一个整数,代表 K 倍区间的数目。
数据范围
1≤N,K≤100000,
1≤Ai≤100000
输入样例:
5 2
1
2
3
4
5
输出样例:
6使用前缀和的解法
import java.util.Scanner;
public class _10_K倍区间 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
int N = sc.nextInt();
int K = sc.nextInt();
int result = 0;
int[] perFixSum = new int[N + 1];
for (int i = 1; i <= N; i++) {
perFixSum[i] = perFixSum[i - 1] + sc.nextInt();
}
for (int left = 1; left <= N; left++) {
for (int right = left; right <= N; right++) {
if((perFixSum[right]-perFixSum[left-1])%K==0){
result++;
}
}
}
System.out.println(result);
}
}使用线段树的解法
import java.util.Scanner;
public class _10_K倍区间 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
int N = sc.nextInt();
int K = sc.nextInt();
int result = 0;
int[] nums = new int[N];
RangeTree rt = new RangeTree(N);
for (int i = 0; i < N; i++) {
nums[i] = sc.nextInt();
rt.insert(i, nums[i]);
}
for (int left = 0; left < N; left++) {
for (int right = left; right < N; right++) {
if (rt.search(left, right) % K == 0) {
result++;
}
}
}
System.out.println(result);
}
}
class RangeTree {
int curV;
int curL;
int curR;
int curM;
RangeTree left;
RangeTree right;
RangeTree(int length) {
this(0, length - 1);
}
RangeTree(int l, int r) {
curL = l;
curR = r;
curM = curL + (curR - curL) / 2;
if (curL != r) {
left = new RangeTree(curL, curM);
right = new RangeTree(curM + 1, curR);
}
}
void insert(int i, int num) {
curV += num;
if (curL != curR) {
if (i <= curM) {
left.insert(i, num);
} else {
right.insert(i, num);
}
}
}
int search(int tarL, int tarR) {
if (curL == tarR) {
return curV;
} else {
if (tarR <= curM) {
return left.search(tarL, tarR);
} else if (curM < tarL) {
return right.search(tarL, tarR);
} else {
return left.search(tarL, curM) + right.search(curM + 1, tarR);
}
}
}
}